This is one for the scientists reading the blog
Andersen JL, Gesser B, Funder ED, Nielsen CJF, Gotfred-Rasmussen H, Rasmussen MK, Toth R, Gothelf KV, Arthur JSC, Iversen L, Nissen P. Dimethyl fumarate is an allosteric covalent inhibitor of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinases. Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 19;9(1):4344.
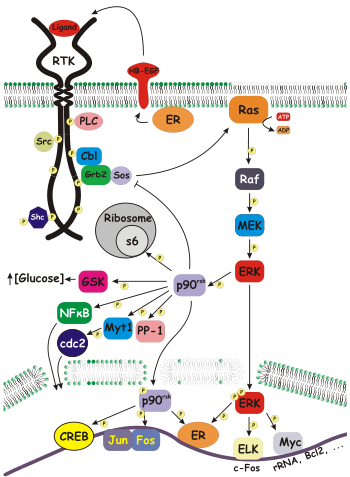
Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) has been applied for decades in the treatment of psoriasis and now also multiple sclerosis. However, the mechanism of action has remained obscure and involves high dose over long time of this small, reactive compound implicating many potential targets (We have no idea how DMF works but they should know that it is believed that the monomethyl fumarate is the active ingredient so should we be bothered about what the dimethyl part binds to? Yes is the answer as it speaks to side-effect potential, but doesn't really tells us how it works). Based on a 1.9 Å resolution crystal structure of the C-terminal kinase domain of the mouse p90 Ribosomal S6 Kinase 2 (RSK2) (an enzyme) inhibited by DMF, we describe a central binding site in RSKs and the closely related Mitogen and Stress-activated Kinases (MSKs). DMF reacts covalently (irreversibily) as a Michael acceptor (nucleophilic addition of a carbanion or another nucleophile to an α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound) to a conserved cysteine (type of amino acid) residue in the αF-helix (curly bit) of RSK/MSKs. Binding of DMF prevents the activation loop of the kinase from engaging substrate (target of the enzyme) , and stabilizes an auto-inhibitory αL-helix, thus pointing to an effective, allosteric (binds to another bit of the molecule rather than the known active site to mediate an effect) mechanism of kinase inhibition. The biochemical and cell biological characteristics of DMF inhibition of RSK/MSKs are consistent with the clinical protocols of DMF treatment.
ribosomal s6 kinase (rsk) is a family of protein kinases involved in signal transduction. There are two subfamilies of rsk, p90rsk, also known as MAPK-activated protein kinase-1 (MAPKAP-K1), and p70rsk, also known as S6-H1 Kinase or simply S6 Kinase. There are three variants of p90rsk in humans, rsk 1-3. Rsks are serine/threonine kinases and are activated by the MAPK/ERK pathway. There are two known mammalian homologues of S6 Kinase: S6K1 and S6K2.